Annuity Table: Overview, Examples, and Formulas
If you receive and invest $100 today, it will grow over time to be worth more than $100. This fact of financial life is a result of the time value of money, a concept which says it’s more valuable to receive $100 now rather than a year from now. It also means that receiving $100 one year from now is less valuable than receiving that same $100 today. In other words, the $100 received one year from now has a present value that is smaller than $100. The table simplifies this calculation by telling you the present value interest factor, accounting for how your interest rate compounds your initial payment over a number of payment periods. Present value calculations can be complicated to model in spreadsheets because they involve the compounding of interest, which means the interest on your money earns interest.
- Simply select the correct interest rate and number of periods to find your factor in the intersecting cell.
- Julia Kagan is a financial/consumer journalist and former senior editor, personal finance, of Investopedia.
- If you don’t have access to an electronic financial calculator or software, an easy way to calculate present value amounts is to use present value tables.
- If the winner was to invest all of his lottery prize money, he would have [latex]\$2,544,543.22[/latex] after [latex]25[/latex] years.
- This variance in when the payments are made results in different present and future value calculations.
Why $1M Is No Longer Enough for Retirement
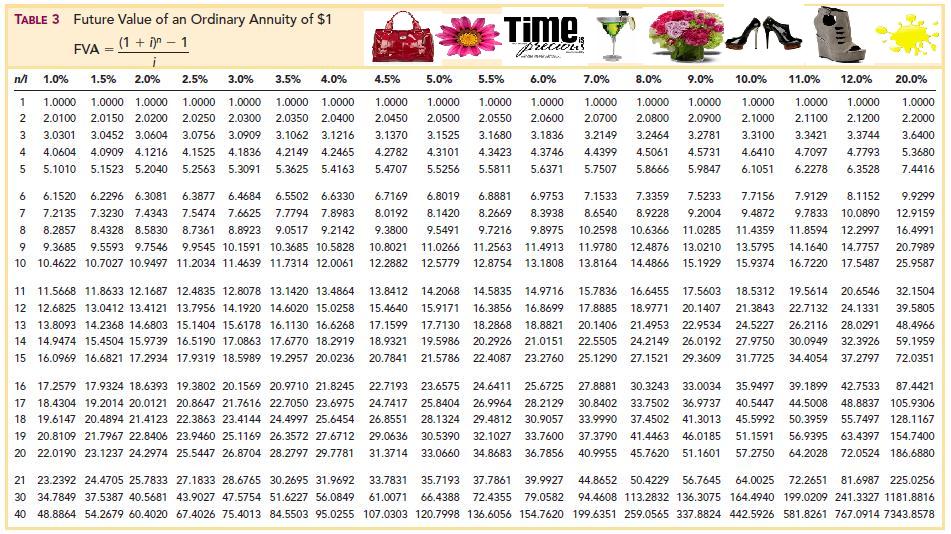
The present value calculation considers the annuity’s discount rate, affecting its current worth. The factor is determined by the interest rate (r in the formula) and the number of periods in which payments will be made (n in the formula). In an annuity table, the number of periods is commonly depicted down the left column. Simply select the correct interest rate and number of periods to find your factor in the intersecting cell. That factor is then multiplied by the dollar amount of the annuity payment to arrive at the present value of the ordinary annuity.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
In year two the account balance will earn $63.60 (not $60.00) because 6% interest is earned on $1,060. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. If you’re interested in buying an annuity, a representative will provide you with a free, no-obligation quote. You could find the exact present value of your remaining payments by using a spreadsheet, as shown below. However, as required by the new California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), you may record your preference to view or remove your personal information by completing the form below.
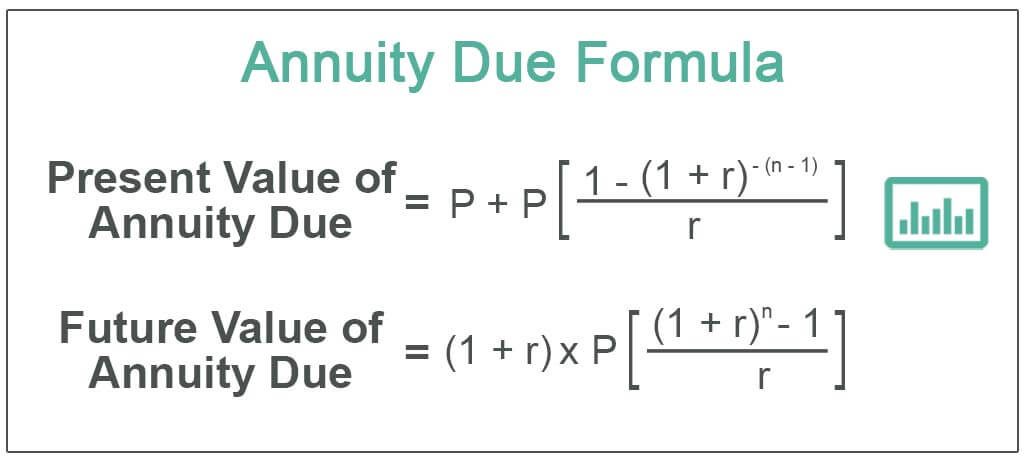
\boxed2.3[/latex] Future Value of Annuities Due
It’s also important to note that the value of distant payments is less to purchasing companies due to economic factors. The sooner a payment is owed to you, the more money you’ll get for that payment. For example, payments scheduled to arrive in the next what is a three-way match in accounts payable gep glossary five years are worth more than payments scheduled 25 years in the future. An ordinary annuity generates payments at the end of the annuity period, while an annuity due is an annuity with the payment expected or paid at the start of the payment period.
You can plug this information into a formula to calculate an annuity’s present value. First, we will calculate the present value (PV) of the annuity given the assumptions regarding the bond. When calculating the present value (PV) of an annuity, one factor to consider is the timing of the payment. As a starting point, let’s have a brief overview of the specific terms you can find in our calculator. When Roberto’s son turns [latex]18[/latex], the trust fund will have a balance of [latex]\$63,672.39[/latex].
When Is The Present Value Of Annuity Calculator Used?
This row’s buttons are different in colour from the rest of the buttons on the keypad. The other two variables are in a secondary menu above the [latex]I/Y[/latex] key and are accessed by pressing 2nd I/Y. Since an annuity’s present value depends on how much money you expect to receive in the future, you should keep the time value of money in mind when calculating the present value of your annuity. Because there are two types of annuities (ordinary annuity and annuity due), there are two ways to calculate present value. Many accounting applications related to the time value of money involve both single amounts and annuities. To demonstrate how to calculate the present value of an annuity, assume that you are offered an investment that pays $2,000 a year at the end of each of the next 10 years.
The FV of money is also calculated using a discount rate, but extends into the future. Present value calculations can also be used to compare the relative value of different annuity options, such as annuities with different payment amounts or different payment schedules. When the calculator is in annuity due mode, a tiny BGN appears in the upper right-hand corner of your calculator. When the calculator is in ordinary annuity mode there is nothing in the upper right-hand corner.
Essentially, in normal interest rate environments, a dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow because it has the ability to earn interest and grow with time. An annuity table provides a factor, based on time, and a discount rate (interest rate) by which an annuity payment can be multiplied to determine its present value. For example, an annuity table could be used to calculate the present value of an annuity that paid $10,000 a year for 15 years if the interest rate is expected to be 3%. An ordinary annuity is a series of equal payments made at the end of consecutive periods over a fixed length of time.
The steps required to solve the future value of an annuity due are identical to those you use for an ordinary annuity except you use the formula for the future value of an annuity due. Altogether, there are seven variables required to complete time value of money calculations. Note that [latex]P/Y[/latex] and [latex]C/Y[/latex] are not main button keys in the [latex]TVM[/latex] row. The P/Y and C/Y variables are located in the secondary function accessed by pressing 2nd I/Y. The effect of the discount rate on the future value of an annuity is the opposite of how it works with the present value.
Get instant access to video lessons taught by experienced investment bankers. Learn financial statement modeling, DCF, M&A, LBO, Comps and Excel shortcuts. The trade-off with fixed annuities is that an owner could miss out on any changes in market conditions that could have been favorable in terms of returns, but fixed annuities do offer more predictability.